Artificial Intelligence or AI – Abstract
Artificial intelligence (aka AI) is a topic that’s been around for decades, but it’s only recently gotten more attention. Artificial intelligence has become essential in our lives, from self-driving cars to virtual assistants like Siri on Apple devices (or Google Assistant on Android) to voice recognition software on smartphones. But there are also concerns about how artificial intelligence will impact society. For example: How will AI affect jobs? Can machines ever honestly think as humans do? What does this mean for privacy? And how can we prevent these issues before they occur?
Artificial Intelligence is the study and development of computer systems that can perform tasks typically requiring human intelligence, such as problem-solving, learning, and decision-making.
Related Article
Artificial intelligence and Machine Learning
What is artificial intelligence?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a broad term for computer systems acting intelligently. It can describe any activity where a computer or machine can perform tasks that would typically require human intelligence. The term was popularized by John McCarthy when he introduced it in 1956 at Dartmouth College. Still, artificial intelligence has been around for decades—the first written work on AI was published in 1946 by Alan M. Turing and Patrick Shaw.
Related: OpenAI ChatGPT
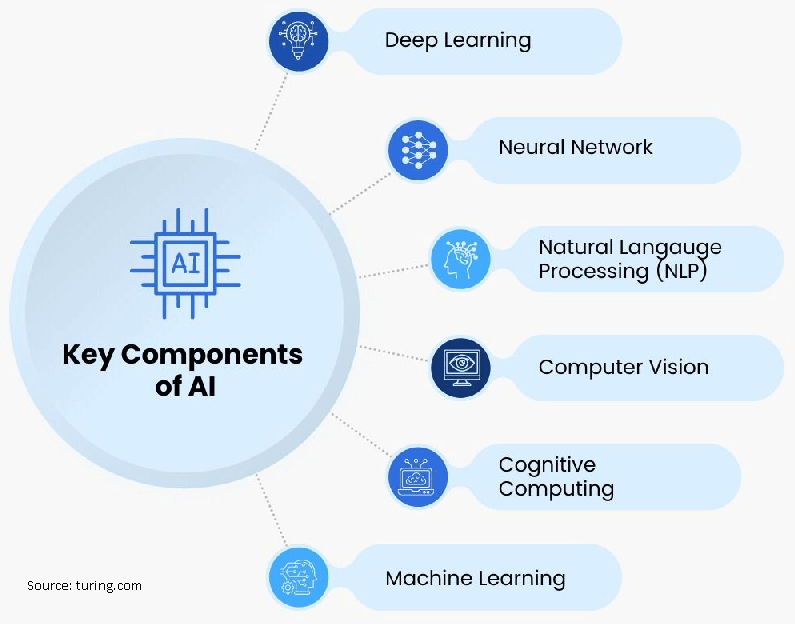
Components of AI
Here are the key components of AI:
- Machine Learning: Machine learning is a subset of AI focusing on algorithms and techniques that allow machines to learn from data and improve their performance over time. It involves training models on labelled or unlabeled data and using statistical techniques to make predictions or take actions based on that learned information. – [ Detailed article: Machine Learning ]
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP is a branch of AI that interacts with computers and human language. It involves understanding and processing natural language in various forms, including speech and text. NLP enables machines to comprehend, interpret, and generate human language, enabling tasks such as language translation, sentiment analysis, chatbots, and voice assistants. [Detailed article on NLP]
- Computer Vision: Computer vision focuses on enabling machines to understand and interpret visual information from images or videos. It involves object detection, image recognition, image segmentation, and scene understanding. Computer vision enables applications like autonomous vehicles, facial recognition, and augmented reality.
- Robotics: Robotics combines AI, sensing, and control technologies to create intelligent machines or robots that can interact with the physical world. AI techniques enable robots to perceive their environment, make decisions, plan actions, and execute tasks. Robotics finds applications in industrial automation, healthcare, and exploration.
- Expert Systems: Expert systems are AI systems that mimic human experts’ decision-making and problem-solving abilities in specific domains. These systems capture expert knowledge in the form of rules, facts, or heuristics and use inference engines to reason and make informed decisions. Expert systems are used in fields like medicine, finance, and engineering to assist with complex decision-making.
- Knowledge Representation: Knowledge representation involves organising and structuring information in a format that machines can understand and reason. It includes techniques such as ontologies, knowledge graphs, semantic networks, and logical frameworks. Knowledge representation enables machines to store, retrieve, and apply knowledge for various AI tasks.
- Planning and Reasoning: Planning and reasoning involve the ability of AI systems to analyze a given situation, consider various actions or solutions, and select the most appropriate course of action. This component deals with logical and probabilistic reasoning, optimization techniques, and decision-making algorithms. Planning and reason are essential for resource allocation, scheduling, and problem-solving applications.
- Neural Networks: Neural networks, also known as artificial neural networks, are computational models inspired by the structure and function of biological brains. They consist of interconnected nodes (neurons) organized in layers, and they learn to recognize patterns and relationships in data through training. Neural networks have proven decisive in tasks like image and speech recognition, natural language processing, etc.
Applications of Artificial Intelligence.
Artificial intelligence is used in many different industries, including:
- Medicine. AI has been used to diagnose cancer and heart disease, among other things. For example, IBM Watson can help physicians determine the most appropriate treatment for patients with certain conditions.
- Law. Judges use artificial intelligence software to help them make decisions more quickly and efficiently than before these programs were developed (for example, Legal Ruling Tool from Lex Machina).
- Education. AI learns from examples of past human behaviour to understand new situations better (for example, IBM’s Watson Internet Service).
Automotive. AI determines whether drivers behave dangerously and may need assistance (for example, Tesla’s Autopilot feature). Real estate. AI can help real estate agents analyze data about potential buyers or renters to recommend the best property for each person (for example, Realty Mogul).
Here are some examples of the practical use of AI.
- AI can help with medical research.
- Predicting climate changes.
- Education and job training.
- AI is also being used to detect crime before it happens.
- AI is being used to filter out spam and other unwanted messages.
The future of artificial intelligence
The future of artificial intelligence is bright. AI is already a massive part of our lives and will only become more pervasive. As we continue to rely on machines for everything from scheduling meetings to writing emails, the potential impact of this technology cannot be overstated, and it’s not just about how much money you’ll save by outsourcing your tasks to an algorithm anymore. In real-life use of AI, DialogFlow is gaining popularity. I will add more references on what Dialogflow is later in this article.
AI will also have an impact on society at large. For example, if you think about it, fewer jobs are available than ever because so many industries have been automated away (or outsourced). This means that even if you’re able-bodied enough to compete in today’s workforce without needing any special training or education beyond high school graduation requirements alone if your job requires physical strength like manual labour or heavy lifting—then chances are good that someone else out there who doesn’t need those same skills might be willing offer them up instead because they get paid better! And while this may sound like bad news given how hard economic times have been lately due mainly to global warming issues caused by climate change initiatives–but eventually things will get better once all these issues are resolved successfully.
Artificial intelligence can be life-changing, but it’s also concerning.
Artificial intelligence is a tool that can be used for good or detrimental. It has the potential to make our lives easier, but it also has the potential to make our lives more difficult. AI is not a deity; it’s simply an effective computer program with specific goals and objectives we humans have created for ourselves.
The good news about artificial intelligence is that it has helped make many things more accessible in our daily lives: from driving cars safely on busy roads (autonomous vehicles) to helping diagnose diseases faster than ever before (medical research). But there are also some downsides associated with using this technology:
- Increasingly sophisticated algorithms are being used by criminal gangs who use them as weapons against us all over social media platforms like Facebook or Twitter; they do this by posting fake news articles explicitly designed so they can spread misinformation while masking their identity behind fake profiles.
Conclusion
Artificial intelligence has been around for a long time. It’s been used as a tool for decision-making, but now it’s being used in a much more human-like way. That means that artificial intelligence is becoming an essential part of our lives on both personal and professional levels. It will help us make decisions and learn from them without relying on humans. With so many different types of artificial intelligence today (traditional AI, machine learning algorithms), you may wonder which best suits your needs. We’re going to discuss some standard features of these algorithms here today so that when looking into whether your business should use artificial intelligence or not, or if they already do, you can make informed decisions about how best fit it into their operation strategy!
References:
- AI Technology topics
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/John_McCarthy_(computer_scientist)
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Artificial_intelligence
- https://ai.google/
- https://www.collegelib.com/what-is-ai/
- https://www.collegelib.com/openai-chat-gpt-technology/
- What is DialogFlow – https://cloud.google.com/dialogflow/docs
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dialogflow
- https://www.collegelib.com/artificial-intelligence-and-machine-learning/
Related articles:
- What 10 things Open AI ChatGPT can / cannot do?
- What is Machine Learning?
- What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
- Artificial intelligence and Machine Learning
- ChatGPT Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF AI)
Collegelib.com prepared and published this curated report on AI / Artificial Intelligence for Engineering topic preparation. Before shortlisting your topic, you should do your research in addition to this information. Please include Reference: Collegelib.com and link back to Collegelib in your work.