Abstract
Hydrogen-based mechanical energy systems are gaining importance as a sustainable alternative to conventional fossil fuel-based power systems. This essay discusses the role of hydrogen in mechanical engineering, focusing on its production methods, storage challenges, and utilisation in engines, turbines, and fuel cell systems. It also highlights the relevance of hydrogen energy in the Indian context, along with the key challenges and future opportunities associated with adopting hydrogen-based mechanical energy systems.
Related: Hydrogen Refuelling Infrastructure Design
Hydrogen-Based Mechanical Energy Systems Seminar Report
Hydrogen-based mechanical energy systems have emerged as a promising solution to meet the growing global demand for clean and sustainable energy. With increasing concerns about climate change, fossil fuel depletion, and environmental pollution, engineers and researchers are actively exploring alternative energy sources. Hydrogen, being the most abundant element in the universe, offers a high energy density and produces only water as a by-product when used as a fuel, making it an attractive option for future mechanical energy systems.
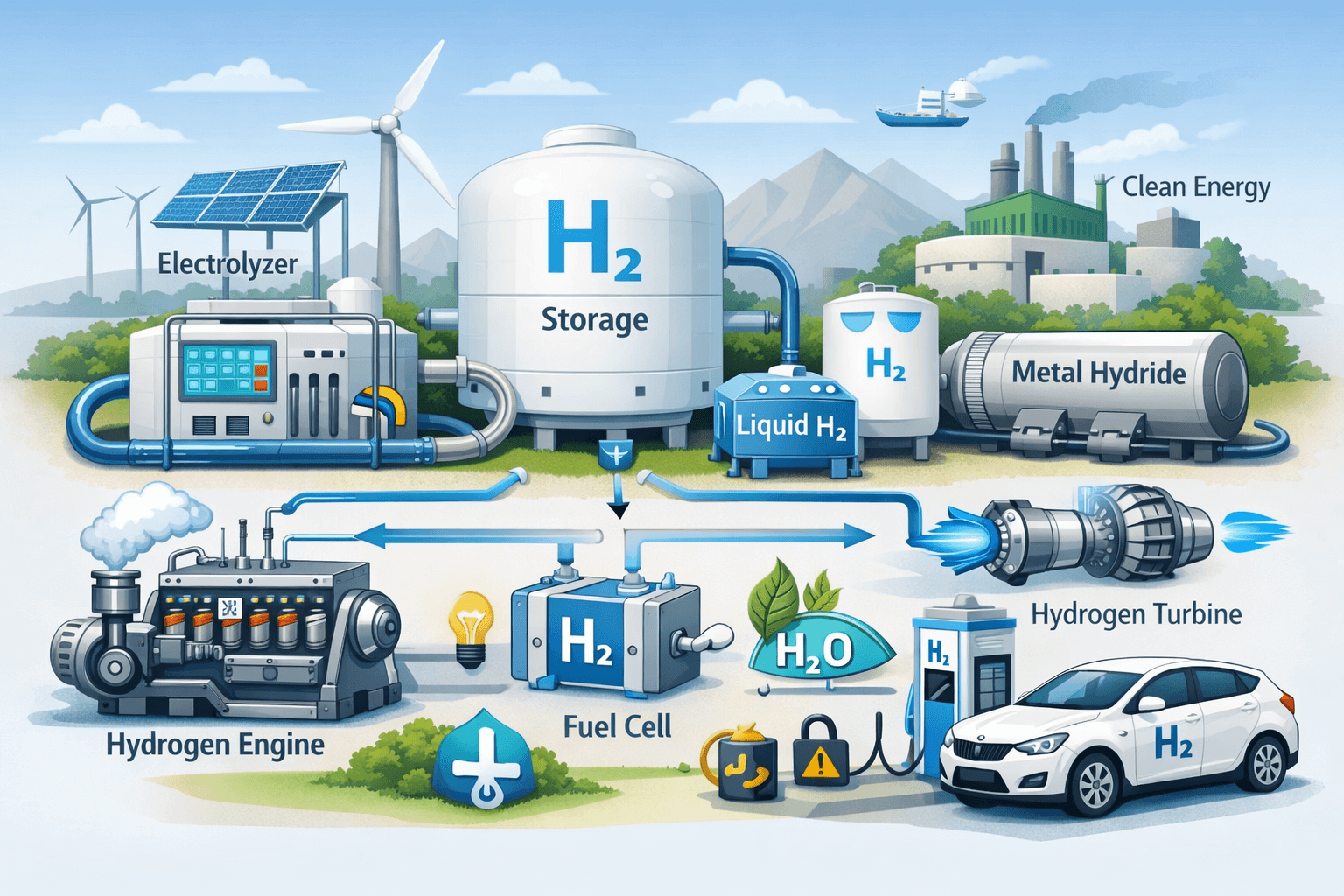
In mechanical engineering, hydrogen-based energy systems primarily focus on the production, storage, and utilisation of hydrogen for power generation and mechanical work. Hydrogen can be produced using methods such as electrolysis of water, steam methane reforming, and biomass gasification. Among these, electrolysis powered by renewable energy sources like solar and wind is gaining attention in India, as it enables the production of green hydrogen without carbon emissions. Mechanical engineers play a key role in designing efficient electrolysers and optimising the overall system performance.
Storage and transportation of hydrogen present significant mechanical challenges due to its low density and high diffusivity. Hydrogen can be stored in compressed gas cylinders, cryogenic liquid form, or through solid-state storage using metal hydrides. Each method requires advanced mechanical design to ensure safety, durability, and energy efficiency. Pressure vessels, valves, and pipelines must be capable of withstanding high pressures and preventing leakage, which demands precise material selection and structural analysis.
Hydrogen-based mechanical energy systems are widely applied in internal combustion engines, gas turbines, and fuel cell systems. Hydrogen internal combustion engines are similar to conventional engines but require modifications in fuel injection and combustion control to handle hydrogen’s fast flame speed. Fuel cells, on the other hand, convert hydrogen directly into electricity through electrochemical reactions, offering higher efficiency and lower noise levels. Mechanical engineers contribute to the design of balance-of-plant components such as compressors, heat exchangers, and cooling systems that support fuel cell operation.
In the Indian context, hydrogen energy has gained strong policy support under national initiatives aimed at reducing carbon emissions and enhancing energy security. Hydrogen-powered buses, trains, and industrial power systems are being tested as alternatives to diesel-based systems. Mechanical energy systems using hydrogen can significantly reduce dependency on imported fossil fuels, while also supporting the transition towards a low-carbon economy. This creates new opportunities for mechanical engineers in research, manufacturing, and system integration.
Despite its advantages, hydrogen-based mechanical energy systems face challenges related to cost, infrastructure, and safety. The high cost of green hydrogen production and the lack of widespread refuelling infrastructure remain major barriers. Additionally, hydrogen’s flammability requires strict safety standards in system design and operation. Continuous research and technological advancements are essential to overcome these limitations.
In conclusion, hydrogen-based mechanical energy systems represent a vital step towards sustainable and environmentally friendly energy solutions. With advancements in production technologies, storage methods, and mechanical system design, hydrogen has the potential to play a major role in future energy systems. For mechanical engineers, this field offers exciting opportunities to contribute to innovation, sustainability, and national development.